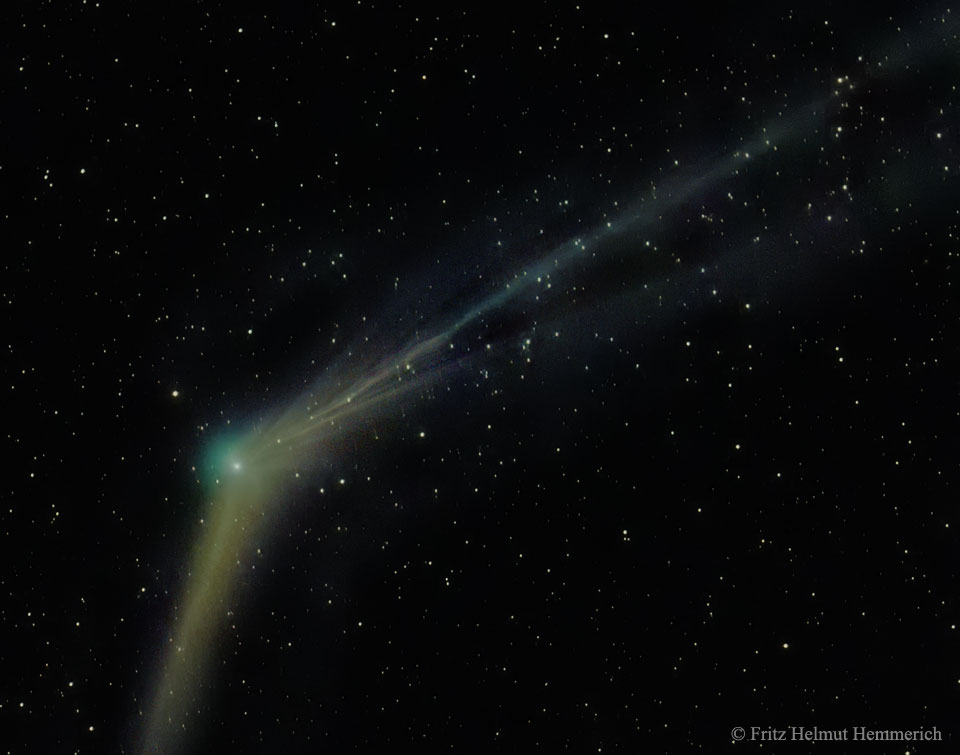

First of all what is a comet? A comet is an irregularly shaped piece or rock and ice that has been trapped by the sun and orbits around it, just like planets but with a more elliptical orbit. This is what comet Catalina is, and right now it is approaching the closest point to the sun ion its orbit, when a comet approaches the closet point to its orbit called the perihelion it starts to warm up and the ice starts to melt, when this happens two different tail grow from it, one is a dust tail and the other is a gas tail. Later one the as the comet get farther and farther it starts to rebuild the ice lost from this encounter, until the next time it get close to the sun again. The dust tail leaves a trail in the path of the comets orbit, while the gas tail ejects in the opposite direction of the sun, so if you see the gas tails direction of a comet, then you can assume the sun is at the opposite direction of the tails path. The gas tail is actually made up of particles that have been ionized by the solar winds from the sun and have been ejected out into space. The actual rock and ice part of the comet is called the nucleus, which when heated up by the sun has its ice go from a solid state directly into a gas state, this causes a huge gas cloud to form around the nucleus called a coma, the coma can grow up to a distance of 100,000 km. There are many more comets that orbit the sun and some can be seen more frequent than others through out the centuries. One fun fact about these is that before anyone new what these actually where, many ancient and semi modern civilizations believed them to be omen of bad luck, which foreshadowed something bad was going to happen, but now a days we know better. (Actual image of Catalina comet taken from North west Africa Canary Island Dec 7, 2015 by Fritz Helmut Hemmerich)
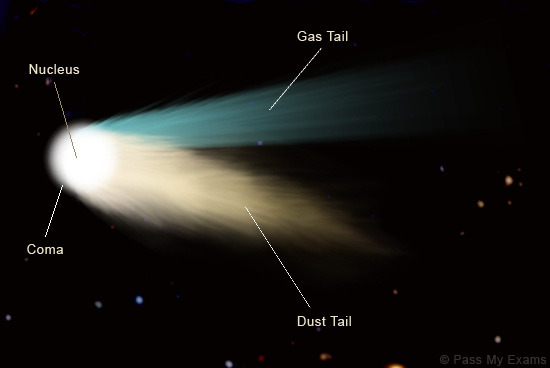 How a comet looks like
How a comet looks like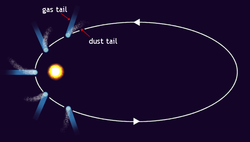 orbit of a comet and phase of closest approach to sun.
orbit of a comet and phase of closest approach to sun.source:
http://apod.nasa.gov/apod/ap151207.html

 From this picture we can see how under the ice cap, there seems to be hydro thermal activity, and with a closer flyby by Cassini we will learn if this kind of activity has created a huge ocean at a global scale, and whether it has created an environment with the ingredients necessary for life. The flyby will provide more information on how habitable the moon really is, and how it behaves geologically and chemically.
From this picture we can see how under the ice cap, there seems to be hydro thermal activity, and with a closer flyby by Cassini we will learn if this kind of activity has created a huge ocean at a global scale, and whether it has created an environment with the ingredients necessary for life. The flyby will provide more information on how habitable the moon really is, and how it behaves geologically and chemically. 